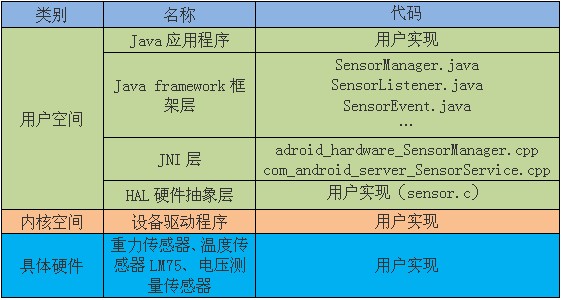
1、Android sensor架构
Android4.0系统内置对传感器的支持达13种,它们分别是:加速度传感器gsensor(accelerometer)、磁力传感器(magnetic field)、方向传感器(orientation)、陀螺仪(gyroscope)、环境光照传感器(light)、压力传感器(pressure)、温度传感器(temperature)和距离传感器(proximity)等。
Android实现传感器系统包括以下几个部分:
各部分之间架构图如下:
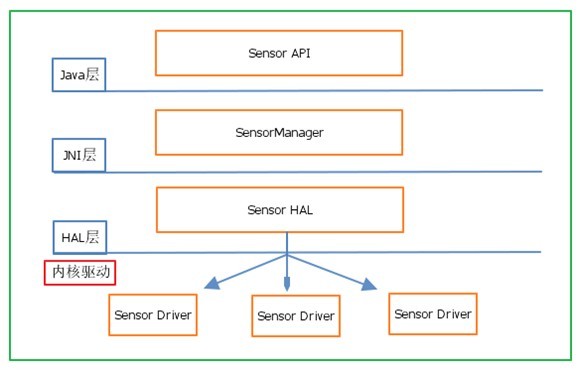
2、Sensor HAL层接口
Google为Sensor提供了统一的HAL接口,不同的硬件厂商需要根据该接口来实现并完成具体的硬件抽象层,Android中Sensor的HAL接口定义在:hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/sensors.h
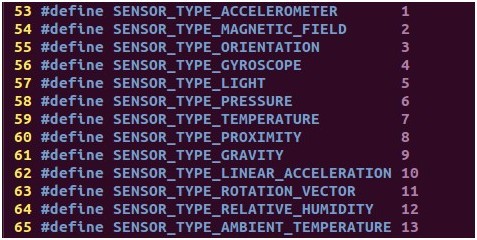
对传感器类型的定义:
传感器模块的定义结构体如下:
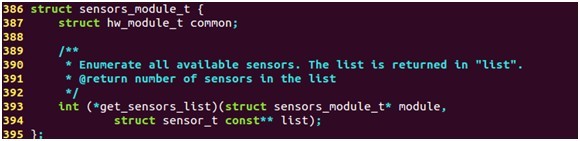
该接口的定义实际上是对标准的硬件模块hw_module_t的一个扩展,增加了一个get_sensors_list函数,用于获取传感器的列表。
对任意一个sensor设备 都会有一个 sensor_t 结构体,其定义如下:
struct sensor_t {
/* name of this sensors */ const char* name; /* vendor of the hardware part */ const char* vendor; /* version of the hardware part + driver. The value of this field * must increase when the driver is updated in a way that changes the * output of this sensor. This is important for fused sensors when the * fusion algorithm is updated. */ int version; /* handle that identifies this sensors. This handle is used to activate * and deactivate this sensor. The value of the handle must be 8 bits * in this version of the API. */ int handle; /* this sensor's type. */ int type; /* maximaum range of this sensor's value in SI units */ float maxRange; /* smallest difference between two values reported by this sensor */ float resolution; /* rough estimate of this sensor's power consumption in mA */ float power; /* minimum delay allowed between events in microseconds. A value of zero * means that this sensor doesn't report events at a constant rate, but * rather only when a new data is available */ int32_t minDelay; /* reserved fields, must be zero */ void* reserved[8]; };每个传感器的数据由sensors_event_t结构体表示,定义如下:
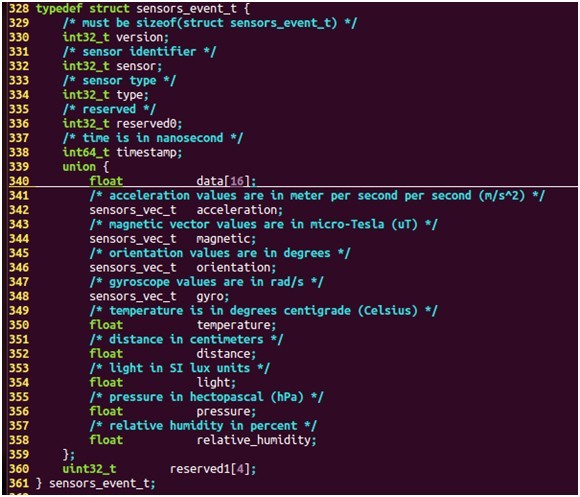
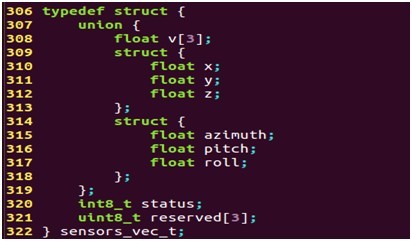
其中,sensor为传感器的标志符,而不同的传感器则采用union方式来表示,sensors_vec_t结构体用来表示不同传感器的数据,sensors_vec_t定义如下:
Sensor设备结构体sensors_poll_device_t,对标准硬件设备hw_device_t 结构体的扩展,主要完成 读取 底层数据,并将数据存储在struct sensors_poll_device_t 结构体中,poll函数用来获取底层数据,调用时将被阻塞 定义如下:
struct sensors_poll_device_t {
struct hw_device_t common; /** Activate/deactivate one sensor. * * @param handle is the handle of the sensor to change. * @param enabled set to 1 to enable, or 0 to disable the sensor. * * @return 0 on success, negative errno code otherwise */ int (*activate)(struct sensors_poll_device_t *dev, int handle, int enabled); /** * Set the delay between sensor events in nanoseconds for a given sensor. * * If the requested value is less than sensor_t::minDelay, then it's * silently clamped to sensor_t::minDelay unless sensor_t::minDelay is * 0, in which case it is clamped to >= 1ms. * * @return 0 if successful, < 0 on error */ int (*setDelay)(struct sensors_poll_device_t *dev, int handle, int64_t ns); /** * Returns an array of sensor data. * This function must block until events are available. * * @return the number of events read on success, or -errno in case of an error. * This function should never return 0 (no event). * */ int (*poll)(struct sensors_poll_device_t *dev, sensors_event_t* data, int count); };
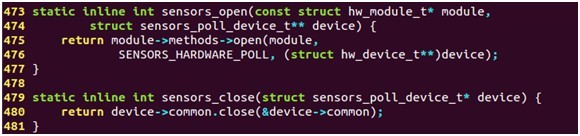
控制设备打开/关闭结构体定义如下:
3、Sensor HAL实现(以LM75温度传感器为例子)
(1)打开设备流程图
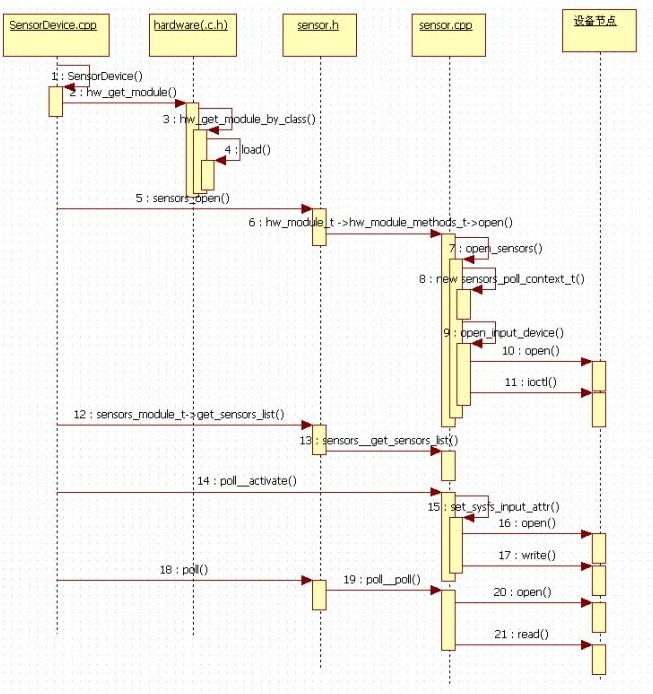
(2)实现代码分析
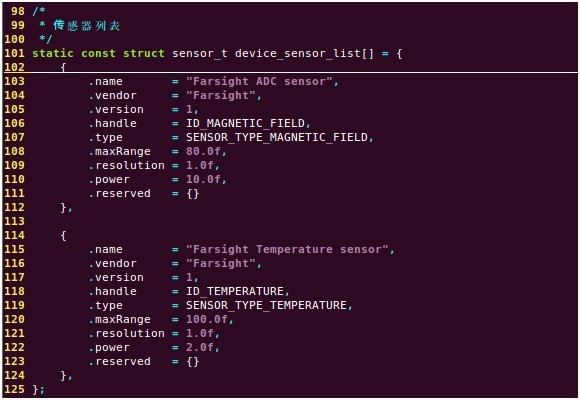
在代码中含有两个传感器ADC电位器和LM75温度传感器,所以在sensor.c中,首先需要 定义 传感器数组 device_sensor_list[],其实就是初始化 struct sensor_t 结构体,初始化如下:
定义open_sensors 函数,来打开Sensor模块,代码如下:
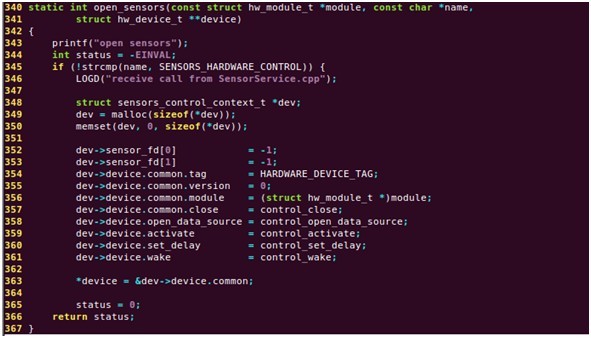
在这个方法中,首先需要为 hw_device_t 分配内存空间,并对其 初始化 为 0,设置重要方法的实现。
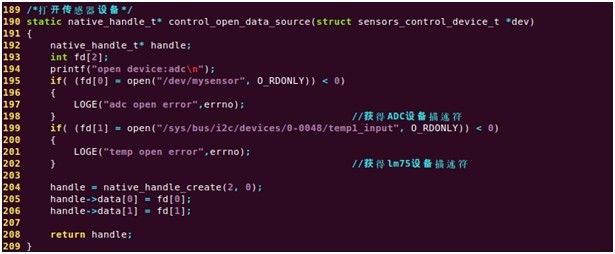
control_open_data_source()打开传感器并使能设备:
调用sensor__data_poll方法读取数据:
/*轮询读取数据*/ static int sensors__data_poll(struct sensors_data_context_t *dev, sensors_data_t * values) { int n; int mag; float temp; char buf[10]; while (1) { if(count % 3 == 2) // 读取ADC值 { if( read(dev->event_fd[0], &mag, sizeof(mag)) < 0) { LOGE("read adc error"); }else{ dev->sensors[ID_MAGNETIC_FIELD].magnetic.v[0] =(float)mag; LOGE("read adc %f\n",(float)mag); *values = dev->sensors[ID_MAGNETIC_FIELD]; values->sensor = ID_MAGNETIC_FIELD; count++; } usleep(500000); return ID_MAGNETIC_FIELD; } else if(count%3 == 1) //读取温度传感器值 { memset(buf, 0 ,sizeof(buf)); if((n = read(dev->event_fd[1], buf, 10)) < 0) { LOGE("read temp error"); }else{ buf[n - 1] = '\0'; temp =(float) (atoi(buf) / 1000); dev->sensors[ID_TEMPERATURE].temperature = temp; LOGE("read temp %f\n",temp); *values = dev->sensors[ID_TEMPERATURE]; values->sensor = ID_TEMPERATURE; count++; } close(dev->event_fd[1]); dev->event_fd[1]= open("/sys/bus/i2c/devices/0-0048/temp1_input", O_RDONLY); usleep(500000); return ID_TEMPERATURE; } else if(count%3 == 0) //读取方向传感器模拟值 { LOGI("read orientation\n"); /* fill up data of orientation */ dev->sensors[ID_ORIENTATION].orientation.azimuth = x + 5; dev->sensors[ID_ORIENTATION].orientation.pitch = y + 5; dev->sensors[ID_ORIENTATION].orientation.roll = z + 5; *values = dev->sensors[ID_ORIENTATION]; values->sensor = ID_ORIENTATION; count++; x += 0.0001; y += 0.0001; z += 0.0001; usleep (500000); return ID_ORIENTATION; } }}